The most important things in a nutshell
.Serie Informationssicherheit
- What is Information Security?
- Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
Importance of information security
.The information security aims to protect information from theft, unauthorized modification or destruction. Information can exist either digitally in IT systems or, for example, in paper form.
What information is worth protecting?
Information worth protecting is often success-relevant and confidential company data such as customer inventories, company strategies, in-house developments or know-how. Due to strict legal requirements, the protection of personal data is particularly important. This includes, for example, the purchasing behavior of the company's own customers or the personal data of its employees.
Protection goals information security
.The main protection goals of IT and information security. (ISO/IEC 27001, IT-Grundschutz , DSGVO) are included:
- Protection of confidentiality (engl. confidentiality; no access to sensitive data for unauthorized third parties),
- Protection of integrity (engl. integrity; no falsification).
- Protection of availability (Engl. availabilty; data are available when they are needed).
Depending on the use case, other protection goals of information security can be included in the consideration.
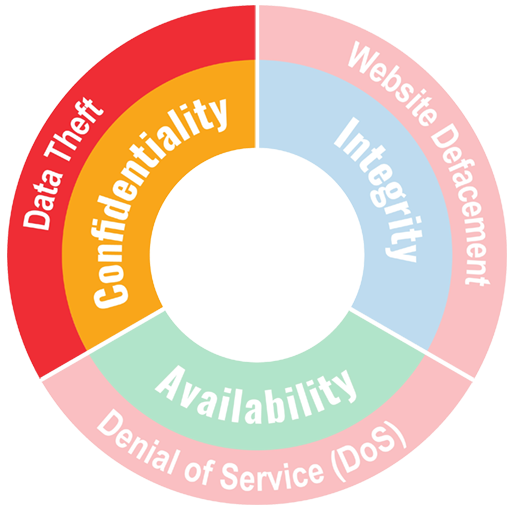
Protection goal confidentiality of information
.In information security, confidentiality means that data is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Examples
Confidentiality attacks:
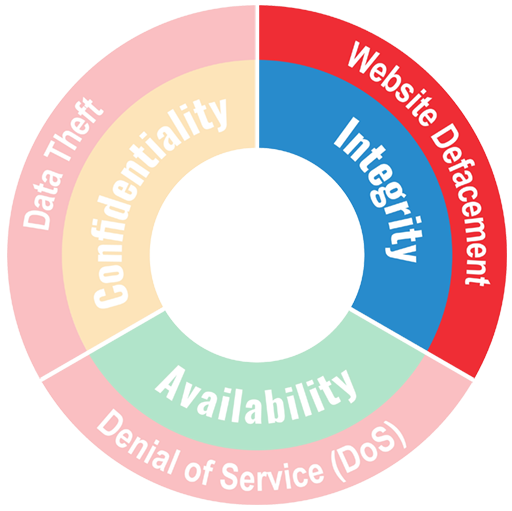
Protection goal integrity of information
.Integrity of data and information means that no unauthorized modification has been made.
Example
Integrity attacks:
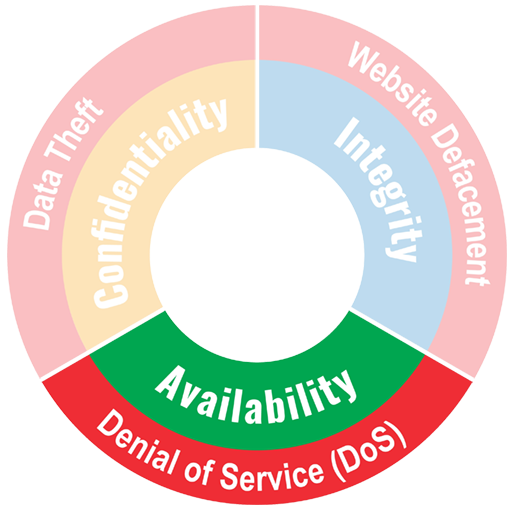
Protection goal availability of information
.Availability of information means that all retrieved information can be used in a timely manner and can be used in accordance with expectations.
Example
Attacks on availability:
Do you need reliable experts to help you protect your IT systems ?
Let's talk about it today!
Other information security protection goals
.
Depending on the use case, in addition to the protection goals of confidentiality, integrity and availability, other protection goals are considered.
Authenticity protection goal
Authenticity refers to both ensuring the identity of the communication partner and ensuring the originator of data. Authenticity is often considered the overriding protection goal. Other protection goals are worthless if it is not possible to determine whether communication is taking place with the desired communication partner.
Example
.The purpose of a username/password login is to ensure that the correct communication partner is on the other end of the line. This simple example also illustrates that in order to achieve the three primary protection goals of information security.
Protection goal of non-repudiation
Non-repudiation is intended to ensure that a communication cannot be subsequently denied to third parties by a party involved. (English: non-repudiation).
Example
- For digital signatures, non-repudiation, along with authenticity, is critical.
- If contracts (online) are concluded, non-repudiation is important for the service provider.
Protection goal bindingness
When authenticity and non-repudiation of a communication are ensured, it is also called binding.
Threats to information security protection goals
.There are hundreds of categories of threats that threaten information security protection goals in one way or another. Below, we cover some of the most important modern threats to protection goals that are current priorities for enterprise security teams.

Inadequately secured or unpatched systems
.The speed and evolution of technology often leads to compromises in security measures. In other cases, systems are developed without regard to security and remain in operation as legacy systems within an organization. Organizations need to identify these poorly secured systems and mitigate the threat by securing, patching, decommissioning or isolating them.
Attacks involving use of social media
.Many people have accounts on social media where they often inadvertently disclose information. Attackers can exploit this type of information to launch attacks.
Social Engineering
In social engineering, attackers manipulate IT system users through psychological triggers such as curiosity or fear to achieve a desired response.
Because the source of a social engineering message usually appears trustworthy, users often click on a link that installs malware on the computer they are using. This exposes personal information, login credentials and other corporate data that the user has access to to the attacker.
Companies can mitigate social engineering by training users to recognize suspicious social engineering messages and forward them to the security team. But technical systems such as email filtering systems can also play a role.
Malware on clients
.Enterprise users work with a variety of endpoints, including mobile devices such as laptops, tablets and smartphones. A key threat to all of these endpoints is malware, which can be transmitted in a variety of ways. It can lead to the compromise of the client itself as well as the extension of privileges to other clients and servers.
Missing mobile device encryption
.Encryption methods encrypt data so that it can only be decrypted by users with secret keys. Using cryptography for encryption is very effective in preventing data loss or corruption when devices are lost or stolen.
Inaccurate or inadequate security configuration of cloud services
.Modern enterprises often use a variety of platforms and cloud services. Almost all of these services have sophisticated built-out security features, but they must be configured and customized by the enterprise to meet its needs. Incorrect or negligent security configuration, or even human error, can easily lead to a serious security incident.
Information security protection goals - what measures can be used to achieve them?
Achieving the protection goals relevant to information security involves both organizational and technical measures.
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is regularly used for the holistic management of information security in the company. In this context, responsibility for information security and the ongoing operation of the ISMS is delegated to an information security officer (ISO).
Content
Releated Content

What is data security? Standards & Technologies
Data security is an important topic for all companies and authorities. Learn more about threats, measures and the legal framework here.
Read more...
Authentication: Differences to authorisation
Authentication and authorization are two words used in IT-Security. They might sound similar but are completely different from each other....
Read more...
Attack Vector and Attack Surface)
An attack vector is a way for attackers to penetrate a network or IT system. Typical attack vectors include ...,
Read more...
Buffer Overflow
A buffer overflow is a programming error that can be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access to IT systems. It is one of the best-known...
Read more...
Cybersecurity concept in 8 steps
A cybersecurity security concept refers to guidelines that are intended to ensure IT security in the company. It is about ensuring the availability,...
Read more...
Proxy Server
A proxy server works as an intermediary between two IT systems. Proxy servers offer different functionalities, improved security and optimised data...
Read more...
What is MITRE ATT&CK?
The MITRE ATT&CK Framework is a continuously updated knowledge base consisting of cyber attacker tactics and techniques across the attack lifecycle.
Read more...
Endpoint Security
A proxy server works as an intermediary between two IT systems. Proxy servers offer different functionalities, improved security and optimised data...
Read more...
Need to Know Principle
The need-to-know principle describes a security objective for confidential information. Access should only be granted to a user if the information is...
Read more...
Top 10 Vulnerability Scanners for 2026
Vulnerability scanners are automated tools that organisations can use to monitor their networks, systems and applications for security weaknesses....
Read more...
NTLM Authentication
In this article, we explain what NTLM authentication is, how it works, and how it can be exploited by attackers.
Read more...
Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) defines methods to ensure information security in an organisation.
Read more...
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System)
The CVSS Score provides a numerical representation (0.0 to 10.0) of the severity of a security vulnerability in IT. We explain how the Common...
Read more...
CIS Controls - A Quick Overview of CIS Controls
The CIS Critical Security Controls (CIS Controls) are a prioritized list of protective measures to defend against the most common cyber attacks on IT...
Read more...
Penetration Tester Career Guide
How does one actually become a pentester? What does a pentester earn? Do career changers also have a chance? And what does a penetration tester do all...
Read more...
Firewalls & Firewall-Architecture
How does a firewall actually work? What does a good enterprise firewall architecture look like? To what extent does appropriate network segmentation...
Read more...Have we sparked your interest?
Just give us a call or write us a message!


